Everyone has a different definition of ‘cool.’ But I think it’s safe to say that most will agree that the animals on this list have earned a spot as one of the world’s coolest animals.
Let’s dive in!
Key Facts:
- Some of the coolest animals in the world include sperm whales, cuttlefish, cheetahs, blobfish, and axotols.
- In my opinion, one of the coolest animals in the world is the Great White Shark!
20 Coolest Animals in the World
The Oxford Dictionary defines cool as “used to show that you admire or approve of somebody/something because they are/it is fashionable, attractive and often different.” When it comes to this list of coolest animals, I handpicked creatures that embody this definition.
Without further ado, here’s a look at some of the most unique (aka coolest) animals in the world.
1. Sperm Whales
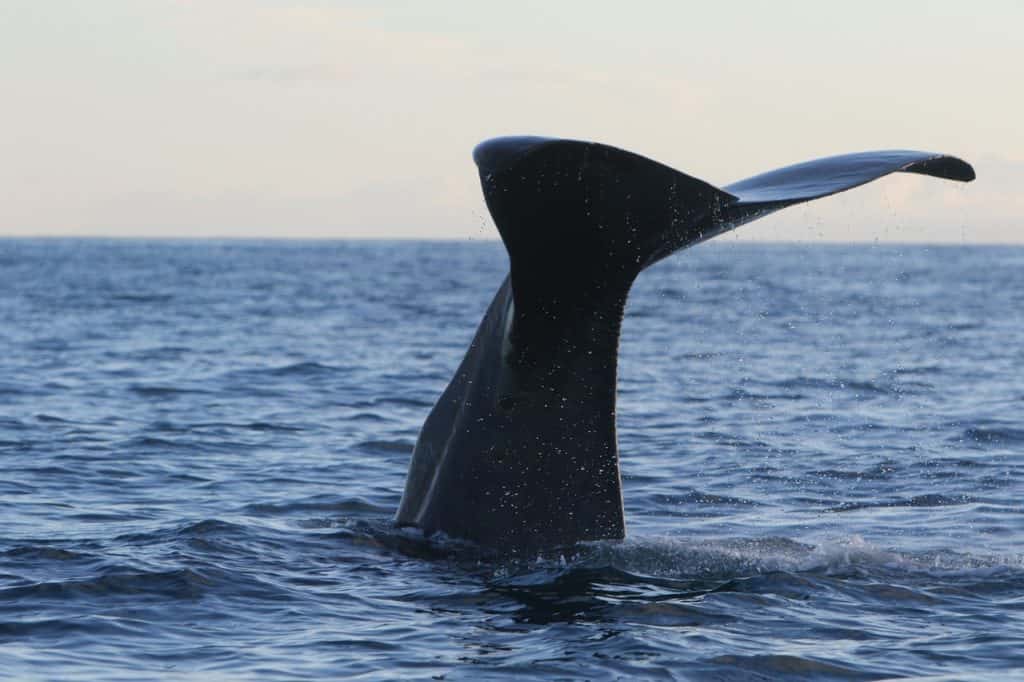

Sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus) are magnificent creatures that dominate the oceans with their sheer size and fascinating adaptations. These giants of the deep can grow up to a staggering length of 60 feet (18 meters) and weigh over 50 tons. Their most distinctive feature is their enormous, block-shaped head, which accounts for one-third of their body length.
One of the most remarkable aspects of sperm whales is their ability to dive to astonishing depths in search of food. These skilled divers can descend up to 3,280 feet (1,000 meters) below the surface, holding their breath for up to 90 minutes, making them the deepest diving mammals on the planet. Their diet primarily consists of giant squid, which they hunt using echolocation, emitting clicks and listening for the echoes to locate their prey.
Interestingly, these creatures also sleep vertically in the water column. While I’ve never witnessed this myself, the pictures make it look like straight out of an eerie spellbook, with these massive animals all hanging vertically for several minutes at a time.
2. African Lungfish
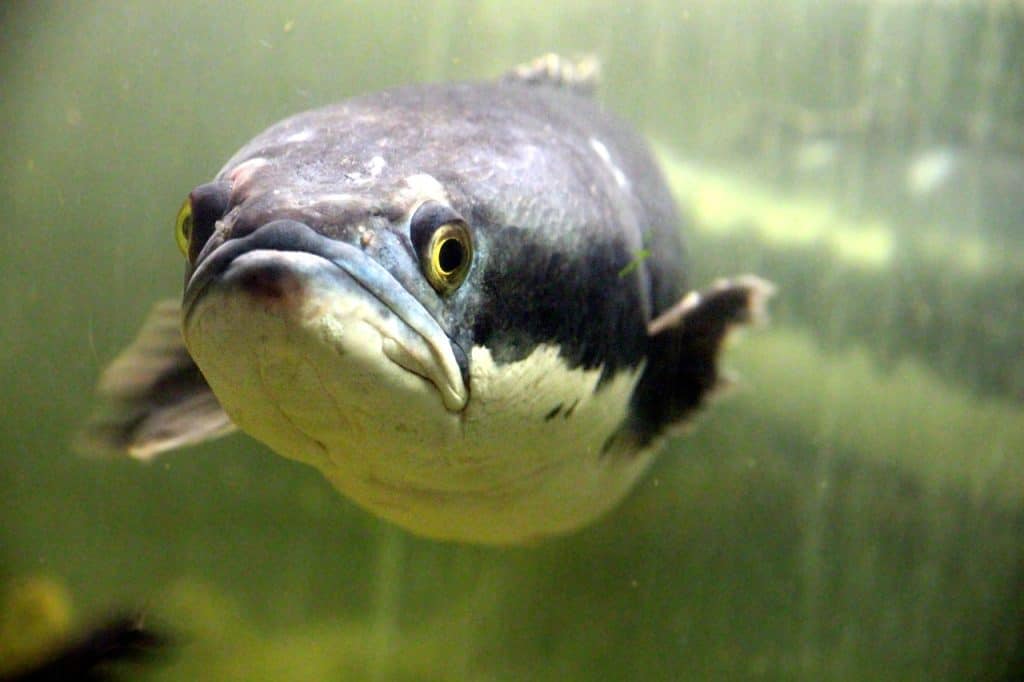

The African lungfish (Protopterus annectens) is an extraordinary creature that showcases the remarkable adaptability of life in aquatic environments. These prehistoric-looking fish can grow between 6 and 40 inches (15 to 101 cm) in length and possess a long, slender body covered in thick scales. What sets them apart is their ability to breathe both through gills and a specialized lung-like organ, allowing them to survive in oxygen-deprived waters or even breathe air when necessary.
One of the most unique features of the African lungfish is their remarkable ability to aestivate, a state of suspended animation similar to hibernation. During periods of drought, when their habitats dry up, they burrow themselves into the mud, secreting a mucus cocoon around their body. Within this protective casing, they can survive for months or even years, awaiting the return of water.
3. Electric Eels
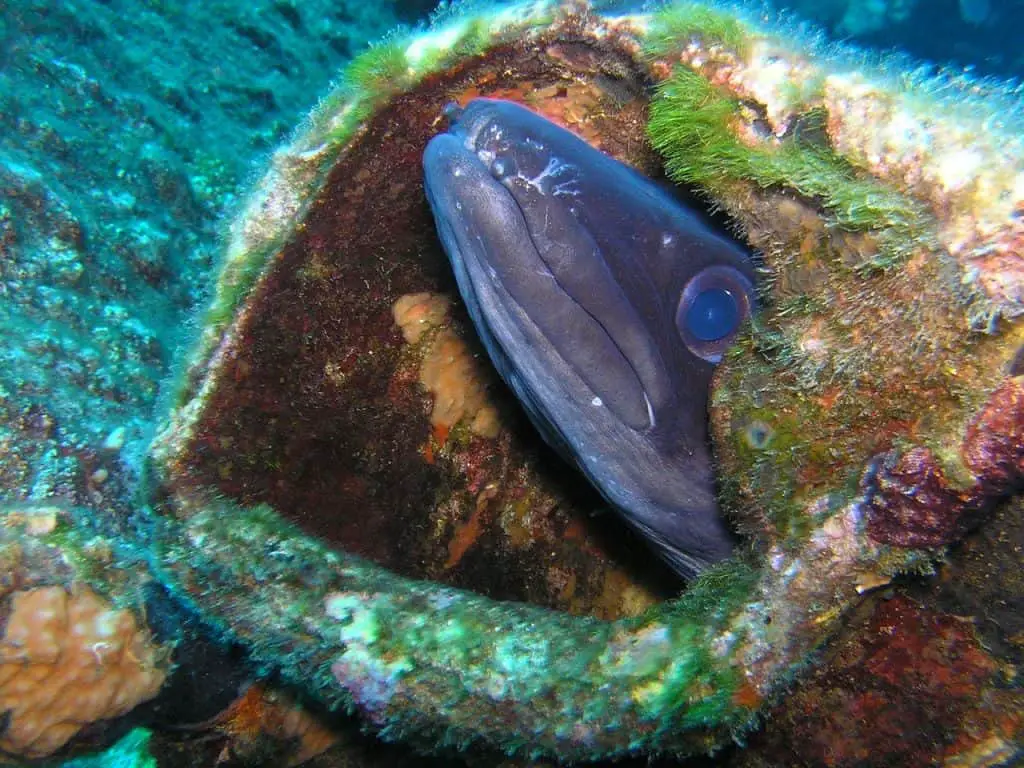

Electric eels (Electrophorus electricus) are captivating creatures that possess an extraordinary ability to generate and discharge electric shocks. Despite their name, they are not true eels but rather a type of electric fish. These remarkable aquatic animals can reach lengths of up to 8 feet (2.5 meters) and have a long, cylindrical body covered in smooth, slimy skin.
What makes electric eels truly unique is their specialized electric organs, which make up around 80% of their body length. These organs consist of specialized cells called electrocytes, capable of producing electric discharges. These discharges serve multiple purposes, including hunting, communication, and self-defense. With their remarkable electrical prowess, electric eels can generate shocks of up to 600 volts, enough to stun or incapacitate their prey.
4. Seahorses
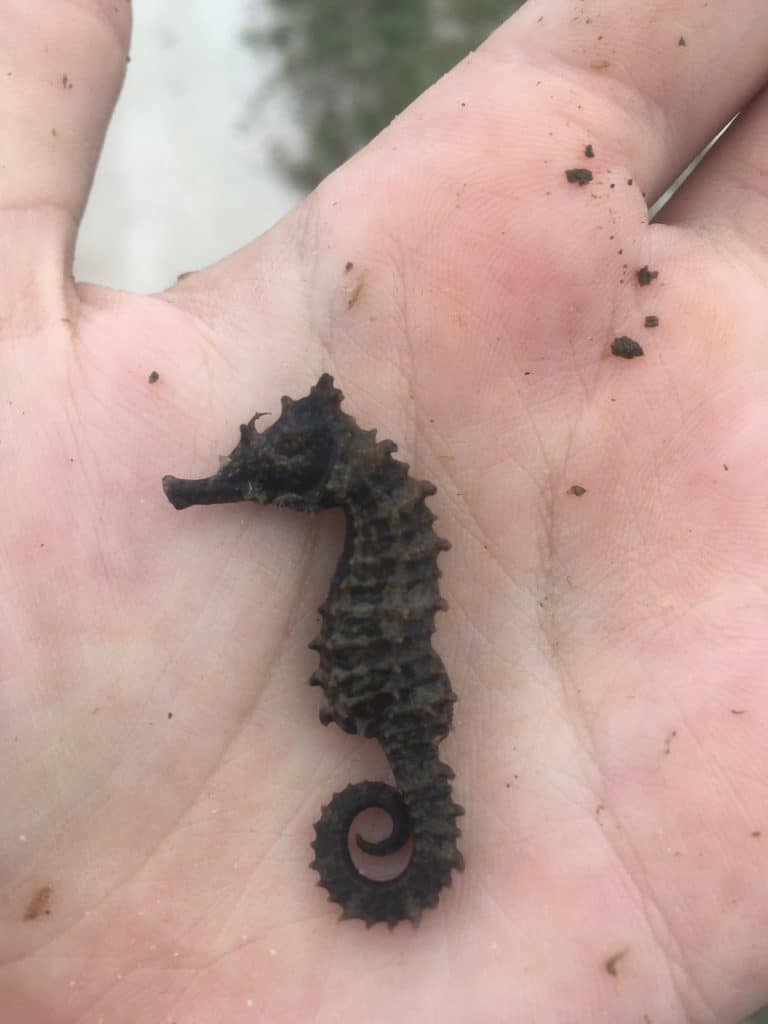

Seahorses, scientifically known as Hippocampus spp., are enchanting creatures that have a peculiar appearance. These small marine fish are characterized by their horse-like head, tubular snout, and curled tail, which they use to cling onto seagrasses and corals. Seahorses exhibit remarkable camouflage abilities, often blending in seamlessly with their surroundings, thanks to their ability to change color.
I’ve often overlooked a seahorse. Sometimes I don’t even notice one until it’s right in front of my face while weaving through seagrass beds. And who knows how many I’ve overlooked!
One of the most remarkable features of seahorses is their unique method of reproduction. Unlike most other fish species, it is the male seahorse that carries and nurtures the developing eggs. After an intricate courtship dance, the female deposits her eggs into a specialized pouch on the male’s belly, where they are fertilized and protected until they hatch. This extraordinary behavior makes seahorses one of the few species in the animal kingdom where males *technically* give birth to live young.
5. Great White Sharks
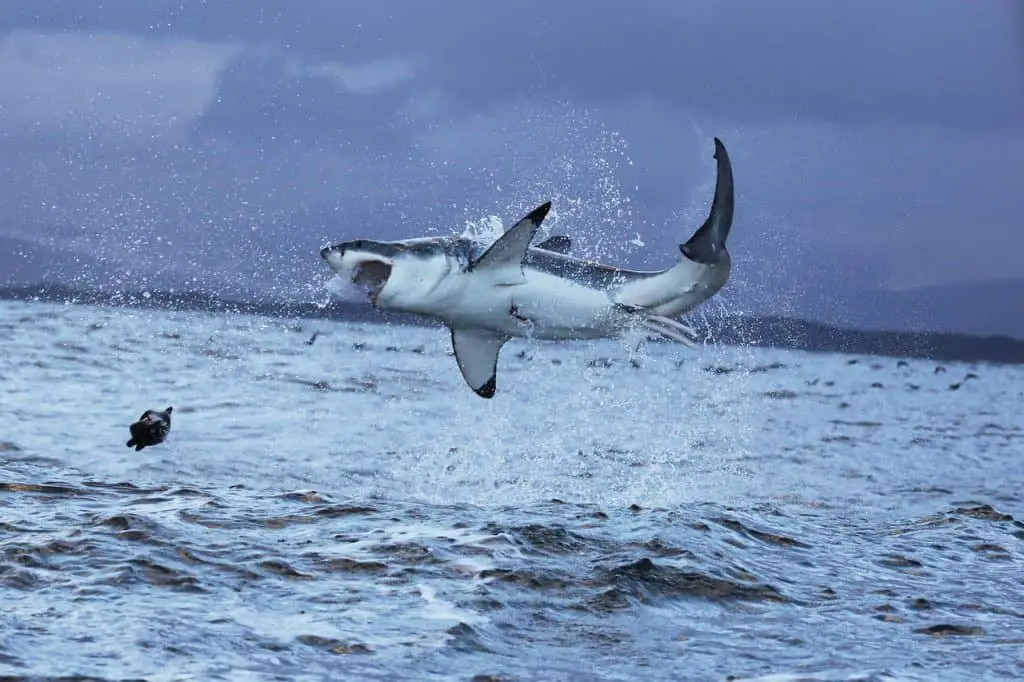

Great white sharks (Carcharodon carcharias) are awe-inspiring creatures that command respect in the world’s oceans. These iconic apex predators are known for their powerful build and intimidating presence. With their torpedo-shaped bodies, massive size reaching up to 20 feet (6 meters) in length, and rows of serrated teeth, they strike a formidable figure.
What sets great white sharks apart is their exceptional hunting prowess and acute senses. They possess an incredible sense of smell, enabling them to detect even a drop of blood in the water from miles away.
The secret behind their powerful sense of smell lies in their specialized olfactory organs called olfactory rosettes. These rosettes are located inside their nasal passages and contain thousands of sensory cells that can detect and analyze various chemical compounds present in the water. Great white sharks can discern a wide range of scents, including blood, fish oils, and other odors associated with potential prey.
Their remarkable speed, reaching up to 35 miles per hour (56 kilometers per hour), allows them to swiftly chase down their prey. Great white sharks also have a unique ability to breach the water’s surface, propelling their massive bodies into the air, which is believed to aid in hunting strategies or social interactions.
6. Axolotls
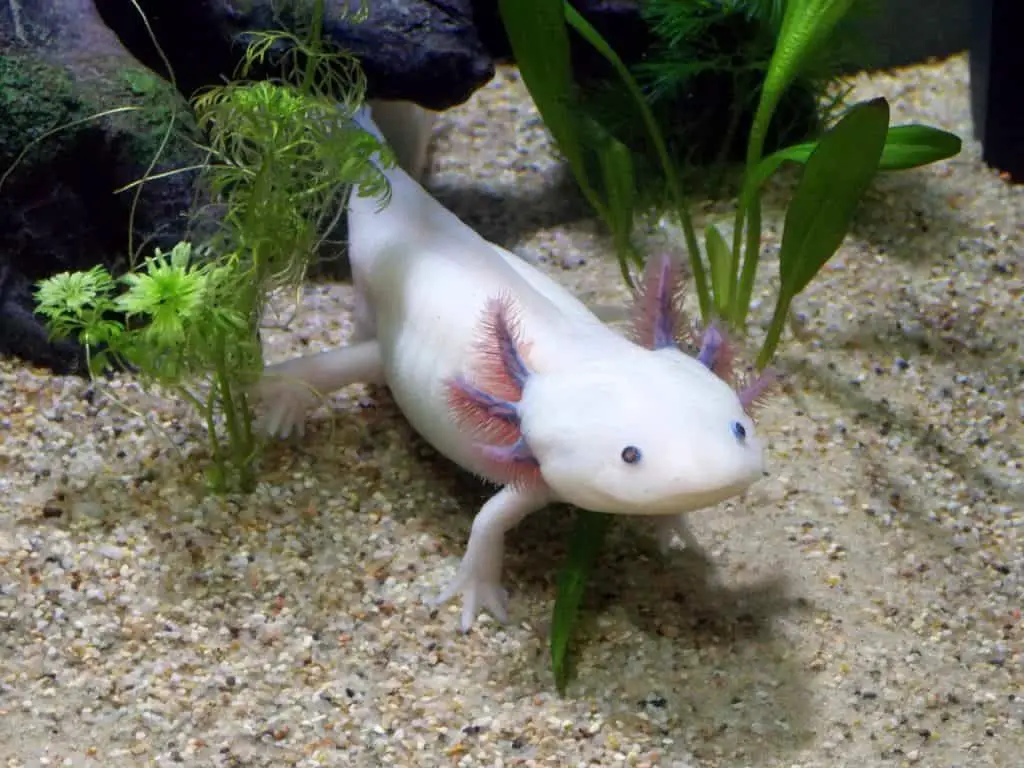

Axolotls, scientifically known as Ambystoma mexicanum, are extraordinary amphibians that defy conventional expectations. With external gills and permanent larval features, they look like perpetual aquatic juveniles. These small creatures typically range from 6 to 18 inches (15 to 45 centimeters) in length and come in various colors, including shades of pink, gray, and black.
What makes axolotls truly remarkable is their ability to regenerate lost body parts. Unlike most amphibians, axolotls retain their juvenile characteristics throughout their lives, including the remarkable capability to regrow limbs, spinal cord, heart tissue, and even parts of their brain. This remarkable regenerative ability is unique and holds potential implications for medical advancements in regenerative medicine.
7. Immortal Jellyfish
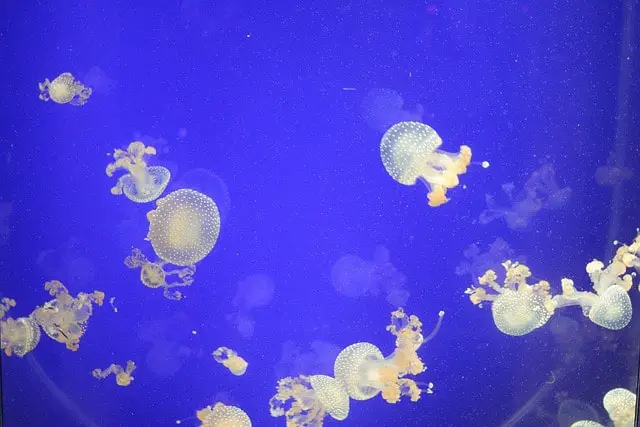

The immortal jellyfish (Turritopsis dohrnii) defies the typical life cycle of most organisms. These small, translucent jellyfish have a bell-shaped body and can reach a size of about 4-5 millimeters. While their appearance may seem unassuming, their unique ability to revert back to an earlier life stage sets them apart.
What makes immortal jellyfish truly fascinating is their remarkable process of “transdifferentiation.” When faced with aging, injury, or stress, these jellyfish have the ability to transform their mature cells into a younger, less specialized state. This rejuvenation process allows them to start their life cycle anew, effectively making them biologically immortal. This extraordinary adaptation has made the immortal jellyfish a subject of great scientific interest.
8. Horned Lizard
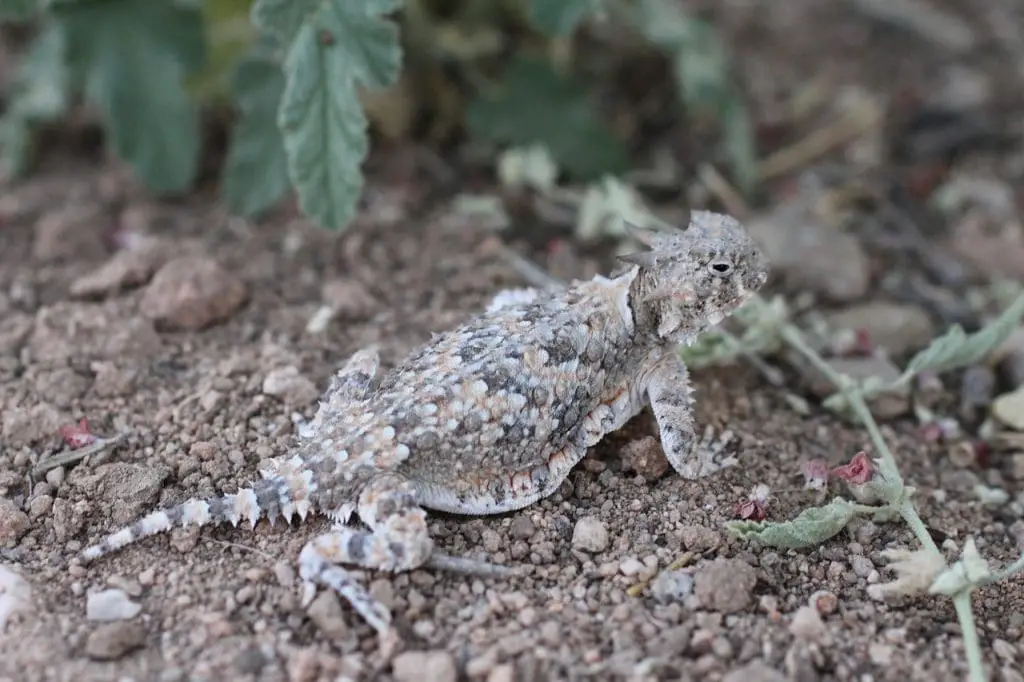

The horned lizard, scientifically known as Phrynosoma spp., stands out with its unique appearance and remarkable defensive adaptations. These small to medium-sized lizards have a flat and wide body, short limbs, and a spiky appearance. Their most notable feature is the array of horn-like projections on their head. The ‘horns’ vary in shape and size among different species.
What makes horned lizards truly unique is their exceptional defense mechanism. When threatened, they have the remarkable ability to shoot blood from their eyes as a deterrent. This behavior, known as “auto hemorrhaging,” involves increasing the blood pressure in the head, rupturing tiny vessels near the eye, and spraying the blood at potential predators. This not only surprises and distracts the predator. But it also exposes them to a foul-tasting substance, making the horned lizard an unappealing meal.
9. Okapi
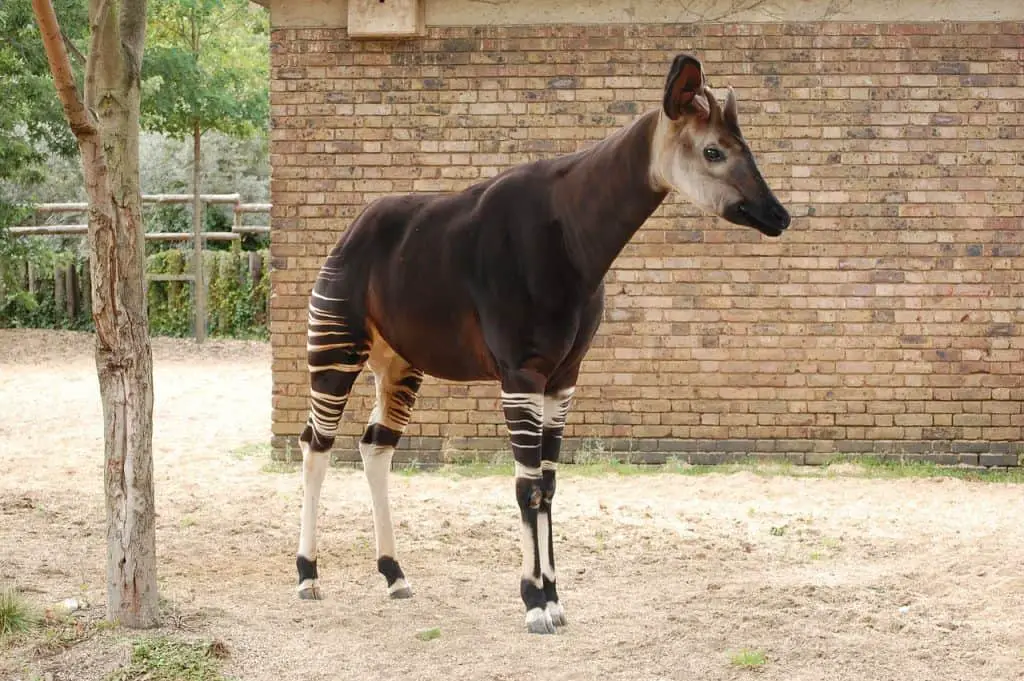
The okapi (Okapia johnstoni) possesses an appearance that combines the characteristics of both giraffes and zebras. But okapi are more closely related to giraffes. These magnificent animals have a rich chocolate-brown coat with striking white stripes on their hindquarters, resembling a zebra’s pattern. Their unique physical features also include a long neck, large ears, and a short, hair-covered ossicone (horn) on their head.
Okapi have an incredibly long and agile tongue, which can extend up to 18 inches (45 centimeters). This adaptation allows them to strip leaves and buds from trees and shrubs.
10. Japanese Spider Crab
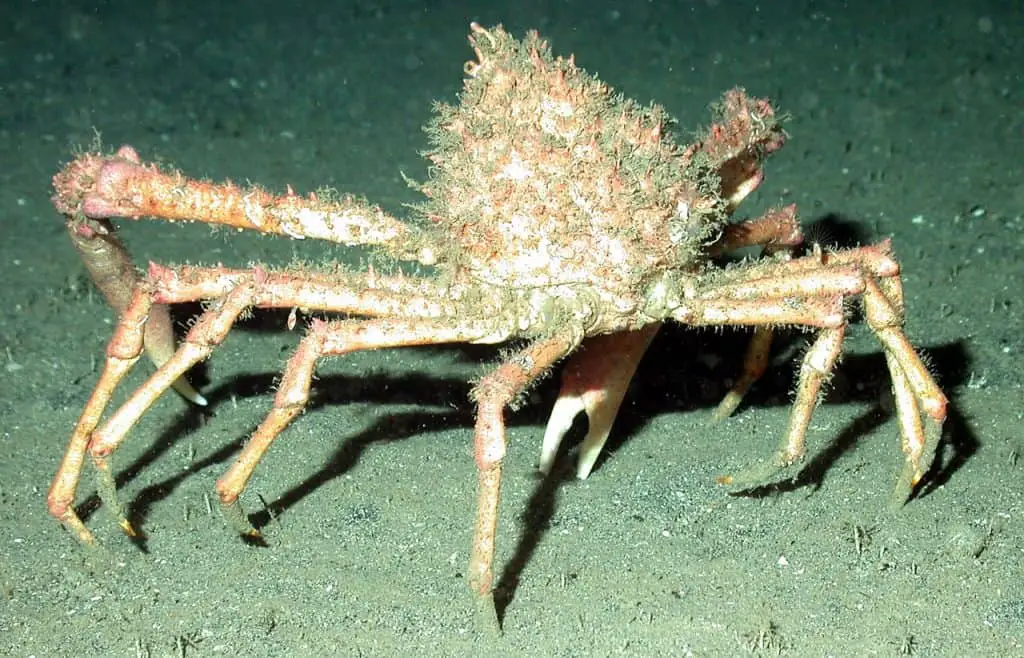

The Japanese spider crab, scientifically known as Macrocheira kaempferi, inhabits the depths of the Pacific Ocean. These colossal crustaceans are known for their impressive size, with leg spans that can reach up to 12 feet (3.7 meters), making them the largest arthropods on Earth. Their bodies are covered in a spiky exoskeleton, which provides protection and aids in camouflage among the rocky seafloor.
The Japanese spider crab has long, slender legs that resemble spider limbs, giving it its name. These legs are not only used for movement but also play a crucial role in capturing prey and defending against predators. Additionally, the Japanese spider crab has the ability to regenerate lost limbs.
11. Blobfish
The blobfish (Psychrolutes marcidus) is an often misunderstood deep-sea dweller. This gelatinous-looking fish is known for its soft, squishy body and a lack of muscle tone. Its unique adaptation allows it to survive in the high-pressure environments of the deep ocean. It lives at depths of up to 4,000 feet (1,200 meters).
What makes the blobfish truly fascinating is its ability to adapt to its extreme habitat. Its gelatinous flesh has a density slightly less than water, enabling it to float effortlessly above the seabed. With a lack of a traditional swim bladder, the blobfish navigates the depths by simply hovering. This allows it to conserve energy in its low-energy environment. While its appearance may seem peculiar, the blobfish’s unique adaptation works well.
12. Cheetah
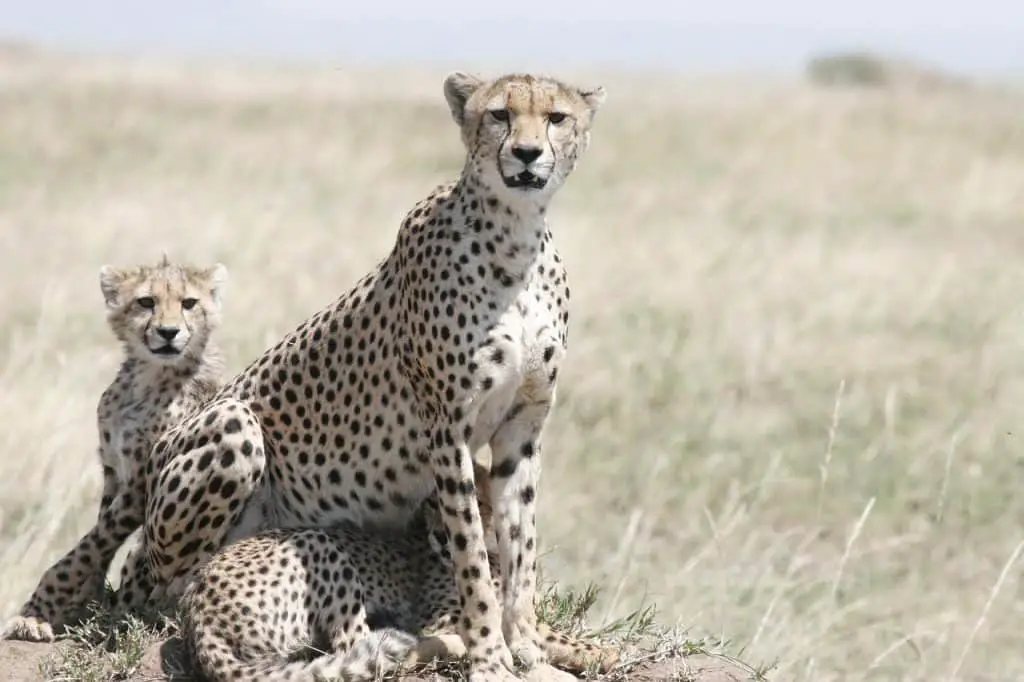

The cheetah, scientifically known as Acinonyx jubatus, is a magnificent and agile big cat. It is renowned for its incredible speed and striking appearance. With its slender body, long legs, and a distinctive coat adorned with black spots, the cheetah is built for speed and camouflage.
As the fastest land animal, it can reach speeds up to 60-70 miles per hour (97-113 kilometers per hour) in short bursts. This allows cheetahs to chase down and capture prey with remarkable precision.
Its lightweight frame, non-retractable claws, and flexible spine provide enhanced agility and traction during high-speed chases. Additionally, cheetahs possess keen eyesight, enabling them to spot prey from great distances.
The cheetah is listed as vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). It faces various threats, including habitat loss, poaching, and conflict with humans. Conservation efforts focus on preserving its natural habitat, implementing anti-poaching measures, and promoting coexistence with local communities.
13. Platypus
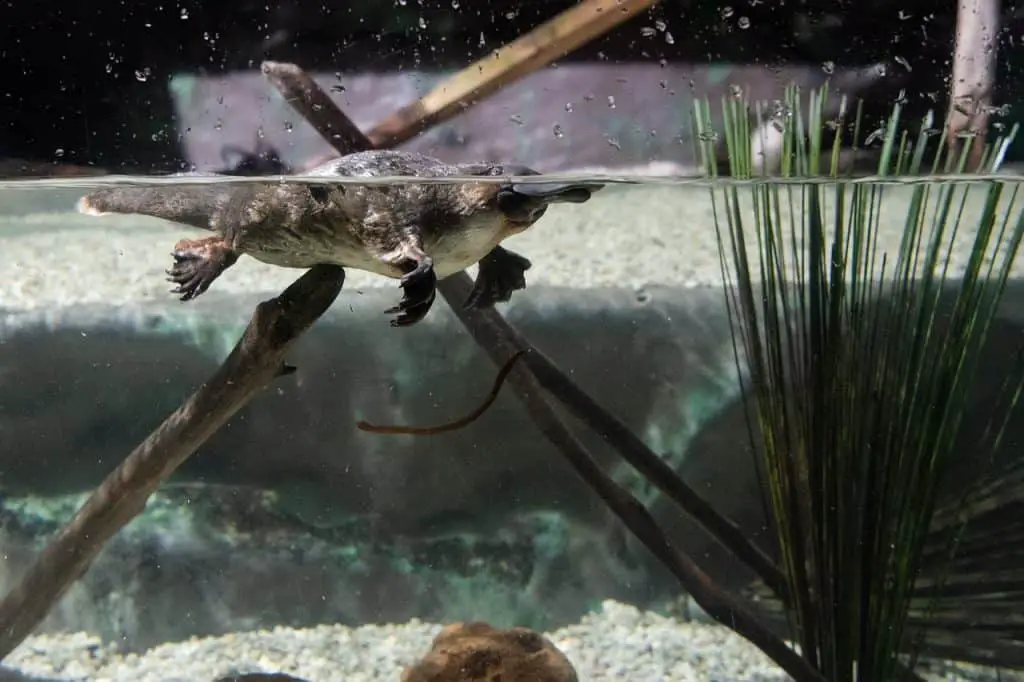

The platypus, scientifically known as Ornithorhynchus anatinus, is an enigmatic mammal native to Australia. It has a beak-like snout similar to a duck, a furry body like a mammal, and webbed feet for efficient swimming. Its flat, paddle-shaped tail serves as a rudder, aiding in navigation through water.
What truly makes the platypus exceptional is its ability to lay eggs despite being a mammal. It is one of the few monotremes. A monotreme is a type of mammal that lays eggs instead of giving birth to live young. Female platypuses have special milk patches that secrete milk, allowing them to nourish their offspring. Furthermore, male platypuses possess venomous spurs on their hind legs, making them one of the few venomous mammals.
14. Cuttlefish
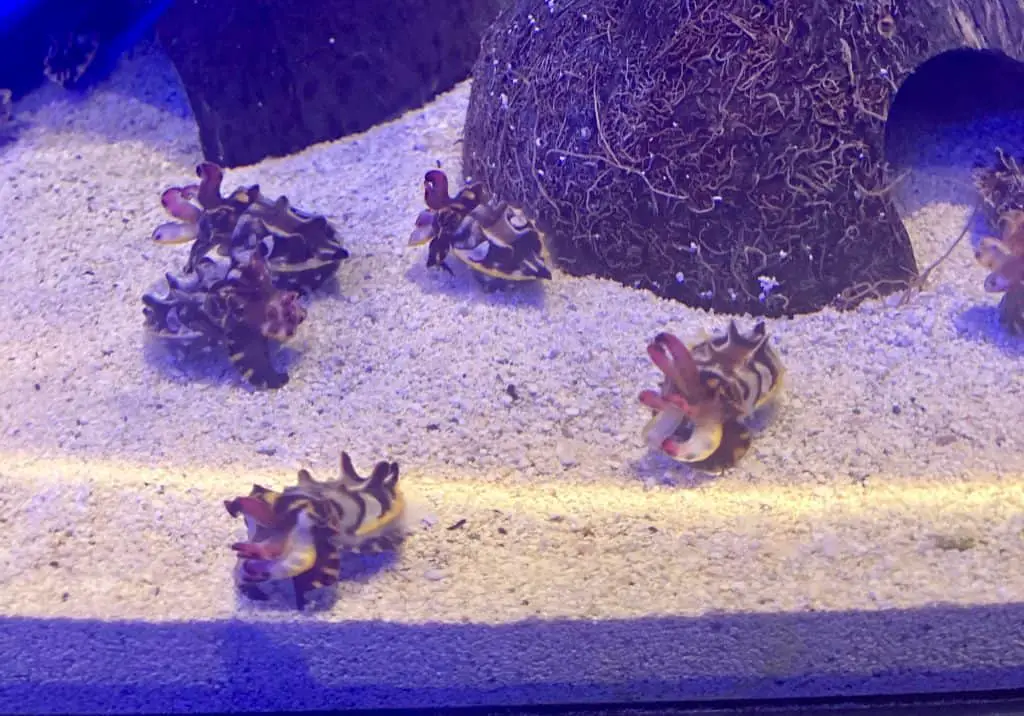

The cuttlefish, scientifically known as Sepia spp., is a mesmerizing marine creature that belongs to the cephalopod family. With its soft body and unique shape, the cuttlefish has a remarkable ability to change color and texture, allowing it to blend seamlessly into its surroundings. It possesses a unique skin structure with specialized cells called chromatophores, which expand and contract to create vibrant displays and intricate patterns.
Notably, cuttlefish is their exceptional camouflage skills. They can rapidly change their color, pattern, and even the texture of their skin to match their environment, enabling them to hide from predators or ambush prey. This remarkable ability makes them masters of disguise and sets them apart as one of nature’s most skilled illusionists.
Pulsing colors make cuttlefish some of the coolest animals in the world!
15. Anglerfish
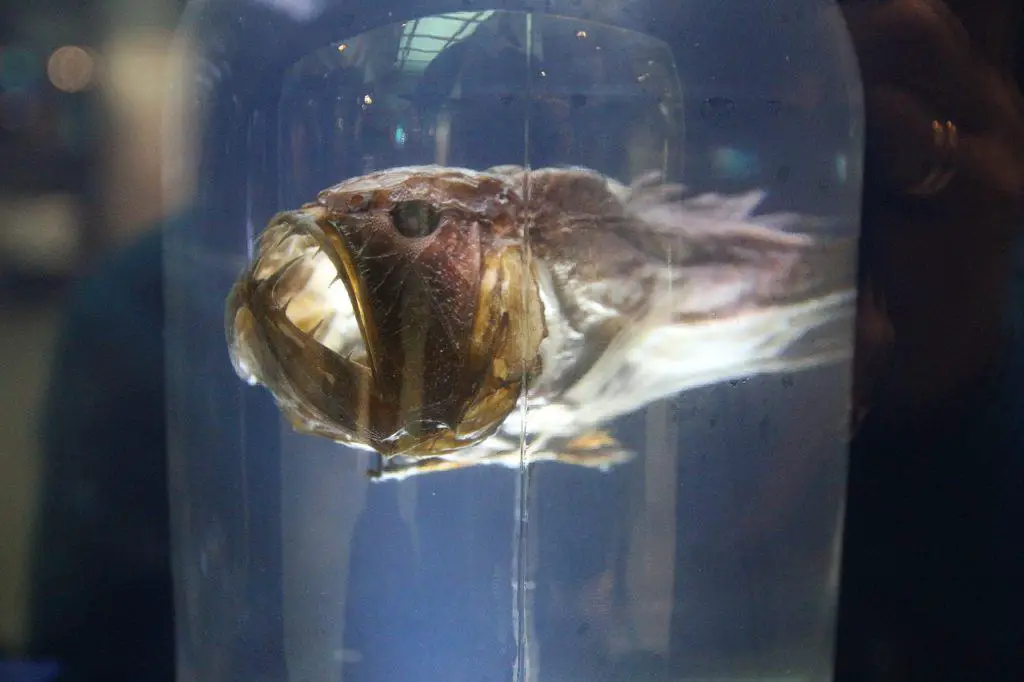

The anglerfish, scientifically known as Lophiiformes, is a bizarre deep-sea creature that has captivated the imagination of researchers and enthusiasts alike. You might have seen it in Finding Nemo! These fish have a large, fleshy growth on their heads known as the illicium or “fishing rod.” At the end of the illicium, there is a bioluminescent lure called the esca, which emits a mesmerizing glow to attract prey in the dark depths of the ocean.
Anglerfish also have a peculiar style of mating. In certain species, the male anglerfish is significantly smaller than the female and lacks the distinctive lure. Once he finds a suitable mate, he latches onto her using specialized jaws and fuses his tissues with hers, becoming a permanent parasitic attachment. This unique adaptation allows the male to provide sperm to the female whenever she is ready to reproduce.
16. Manta Ray
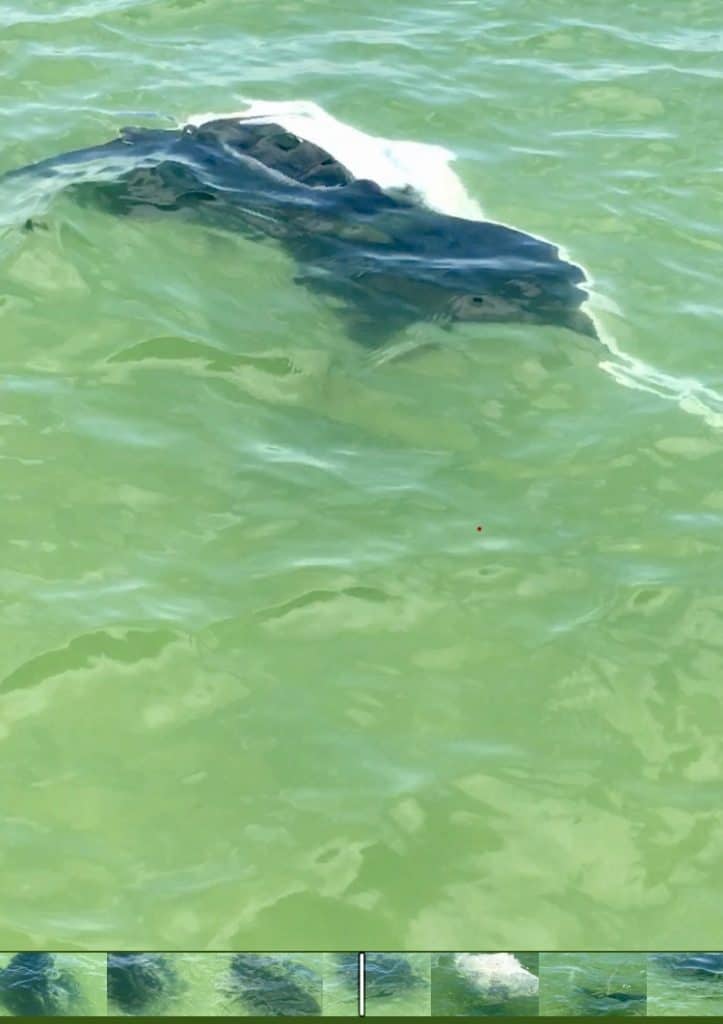

Note: The picture above is of a feeding manta ray. I had the pleasure of watching it feed for around 20 minutes :)
The manta ray (Manta birostris) is a graceful giant of the oceans. Their expansive wingspan can reach up to 25 feet (7.6 meters) or more. So it’s not surprising that these majestic creatures are renowned for their beauty and gentle nature. Manta rays have a unique physical structure, characterized by their flat bodies, elongated cephalic fins, and a distinct lack of a stinging tail, which differentiates them from their stingray relatives.
One of the most remarkable features of these coolest animals is their filter-feeding mechanism. They possess specialized gill rakers that enable them to feed on plankton and small fish by filtering them out of the water as they glide through the ocean. This adaptation allows manta rays to consume vast amounts of microscopic organisms.
17. Octopus
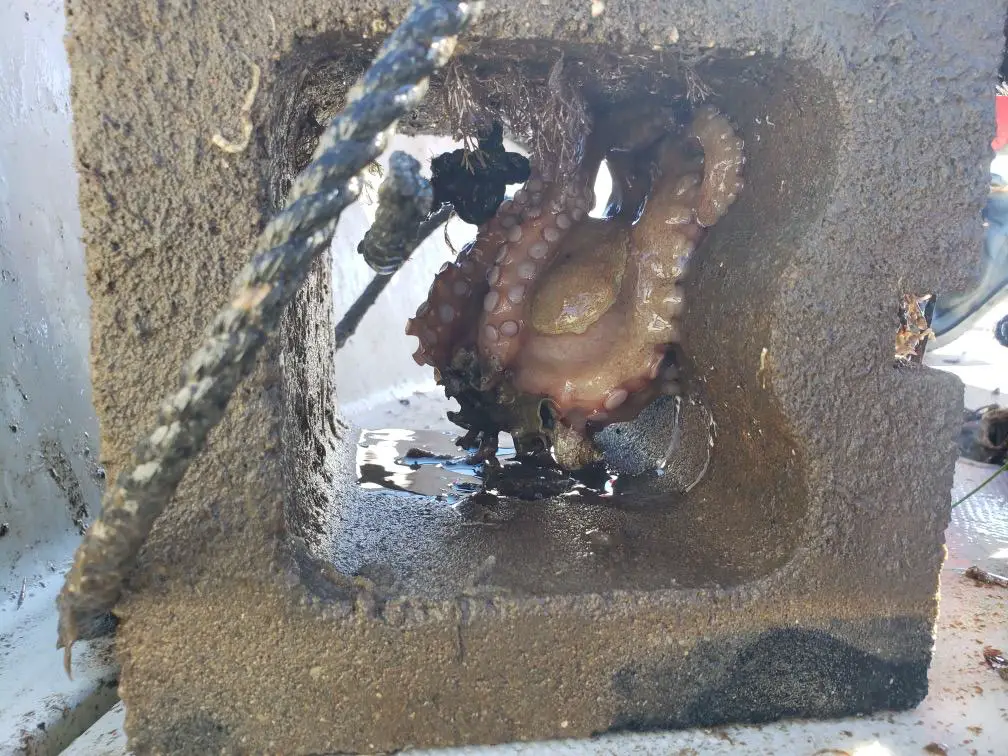

Note: The image above is of an octopus I accidentally pulled onto the boat via this concrete block. I was surprised! But this little guy made it back into the water unharmed :)
The common octopus, scientifically known as Octopus vulgaris, is a highly intelligent creature that dwells in the depths of the ocean. With its soft, gelatinous body and eight arms adorned with suckers, the octopus has a remarkable ability to adapt and camouflage itself within its surroundings. Its extraordinary skill in changing color, texture, and shape allows it to blend seamlessly with rocks, coral, and other marine structures, making it a master of disguise.
What makes the octopus truly unique is its incredible problem-solving abilities and high level of intelligence. These remarkable creatures are known for their complex behaviors, including tool use, problem-solving, and even the ability to mimic other animals. Octopuses also have a remarkable capacity for learning and memory, allowing them to navigate their environment and interact with their surroundings in intricate ways.
When you see an octopus solve a puzzle, it’s hard not to put them on the list of coolest animals.
18. Tasmanian Devil
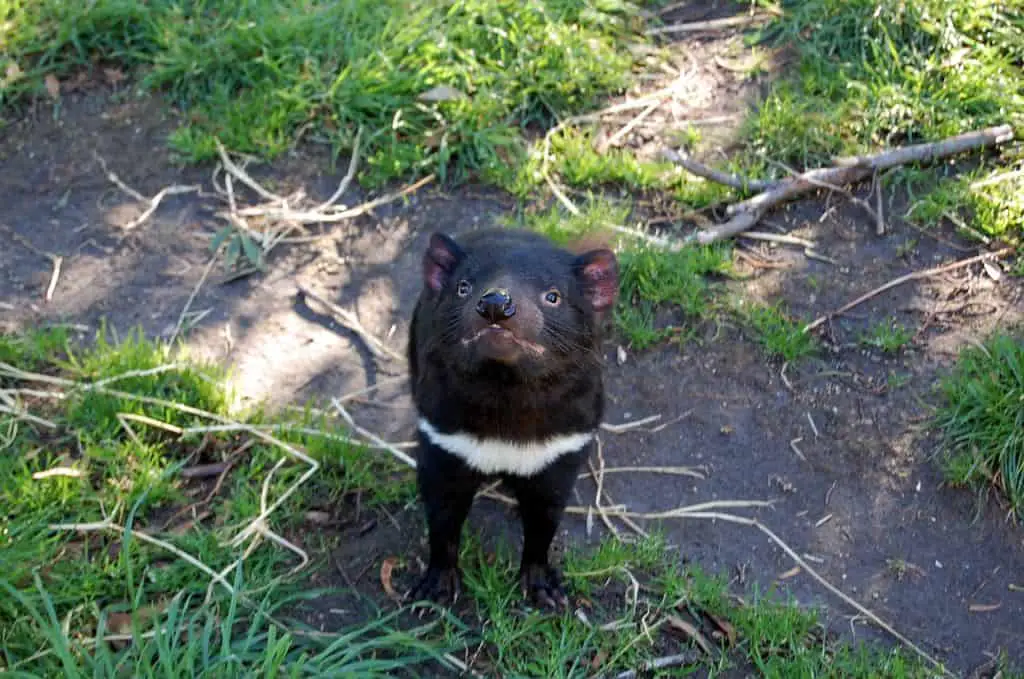

The Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii) is an iconic marsupial native to the island of Tasmania in Australia. These small but robust creatures have a distinct physical appearance, characterized by their stocky build, powerful jaws, and black fur with white markings on their chest. Tasmanian devils are known for their ferocious and aggressive nature, which is evident in their strong bite and loud, eerie vocalizations.
Tasmanian devils possess powerful jaw strength, which allows them to crush bones and consume every part of their prey, including fur, flesh, and even bones. They are scavengers and opportunistic hunters, feeding on a variety of food sources, such as small mammals, birds, reptiles, and carrion. Additionally, Tasmanian devils are the largest surviving carnivorous marsupial, making them a truly cool animal.
19. Giraffe
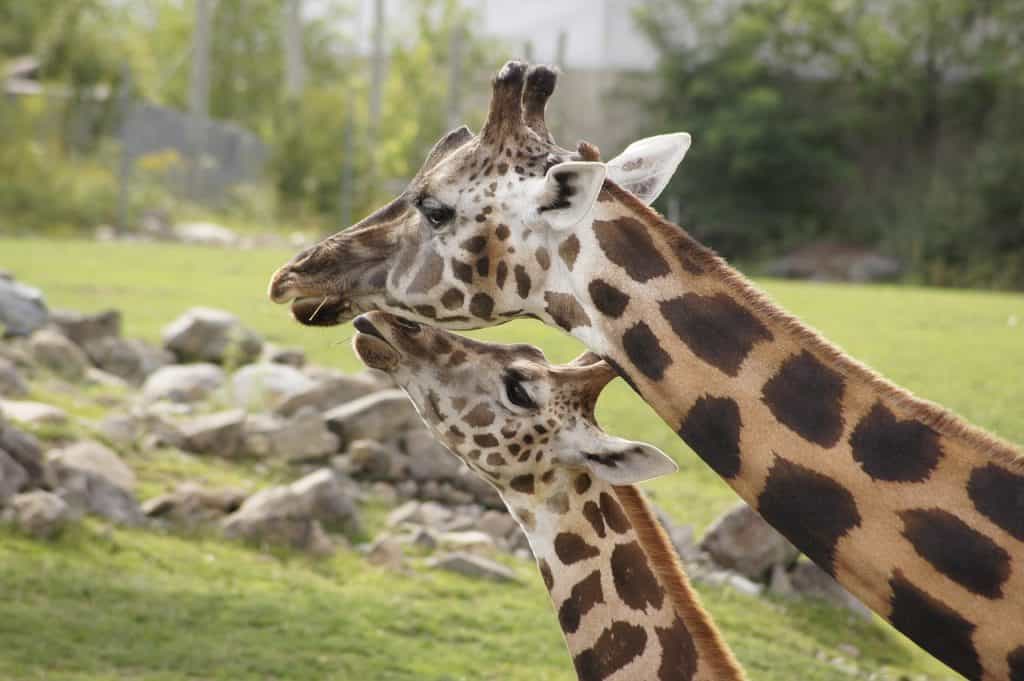

The giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis) is a towering creature that roams the African savannah. With its long neck, towering height, and distinct spotted coat, the giraffe is instantly recognizable. These remarkable animals have a unique physical structure, with their elongated necks and legs, allowing them to browse leaves from tall trees that other herbivores cannot reach.
What makes the giraffe truly extraordinary is its exceptional cardiovascular system. To pump blood up its long neck to reach the brain, the giraffe has a powerful heart that can generate high blood pressure. Additionally, it has specialized valves and thick-walled blood vessels that prevent blood rush when the giraffe lowers its head to drink water. This adaptation enables the giraffe to maintain a steady blood supply to its brain, even in extreme positions.
20. Elephants
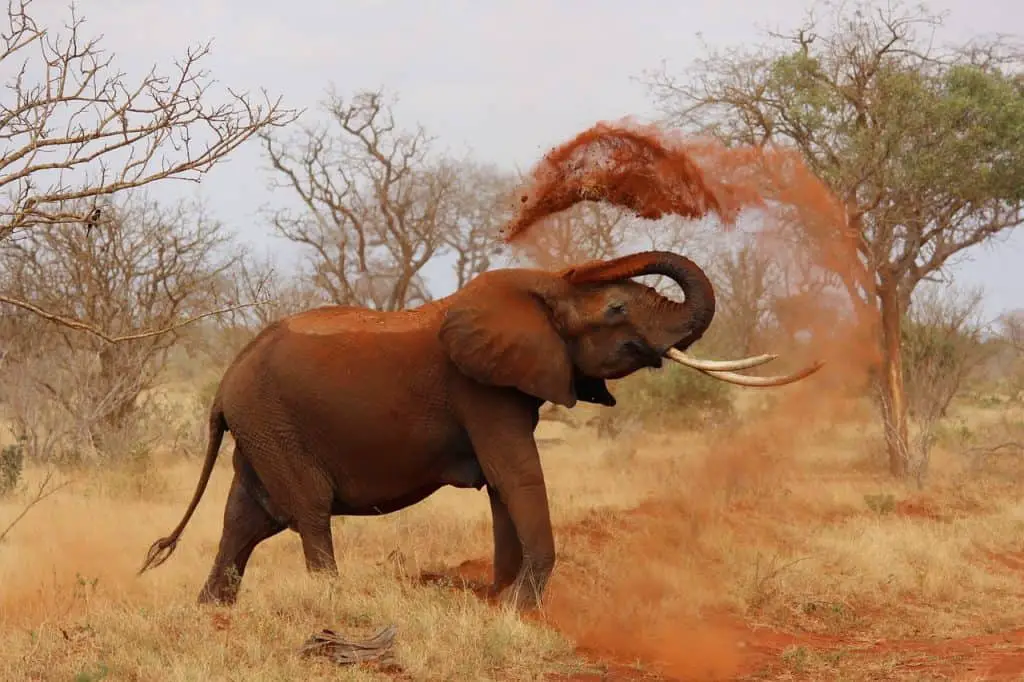

The elephant is scientifically known as Loxodonta (African elephants) and Elephas (Asian elephants). You might know that elephants are highly intelligent creatures that roams the grasslands and forests of Africa and Asia. These gentle giants are known for their massive size, with the African elephant being the largest land animal on Earth. They have long, muscular trunks, large tusks (present in both males and some females), and their characteristic floppy ears.
Elephants boast an incredible memory and social structure, which puts them on this list of coolest animals. They form tight-knit family groups led by a matriarch. Additionally, communicate sophisticated, involving various vocalizations, body movements, and even infrasound. Elephants also exhibit complex emotions and have been observed displaying acts of compassion, grief, and cooperation within their social groups.
Final Take on the World’s Coolest Animals
The creatures that made this list are some of the coolest animals in the world. But, of course, there are plenty of other amazing animals out there. Which do you think is the coolest animal in the world?